Study Systems
Hover over images for more information

Solanum sect. Lycopersicon
includes the domesticated tomato (centre) and a dozen ecologically, phenotypically, and biochemically diverse wild relatives. The wild species are found from Ecuador to Chile along the Andean slopes and north-western coast of South America. (Image: TGRC)

Solanum
Wild tomato species differ in their defense responses to Manduca — a natural herbivore specialist on Solanaceous species. Manduca sexta (tobacco hornworm) on flower buds of Solanum habrochaites. (Image D. Haak)
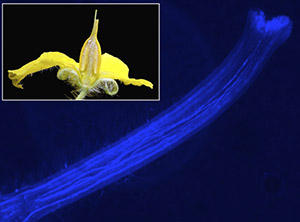
Solanum
A pollinated style (female reproductive tract) from Solanum, stained to visualize pollen tube growth following pollination. Inset: Cross section of S. habrochaites flower. Solanum exhibit mate choice, where pollen can be rejected within the style, depending on their genotype and/or species identity. (Images: CJ Jewell)

Solanum
In vitro assay of pollen tube behavioral responses to ovule chemoattraction. A pollen tube emerges from the base of the style (lower left) and grows across the media toward one of three available ovules. (Image: CJ Jewell)

Solanum
Wild tomatoes have diurnal reproductive behavior, where flowers close in the evening (left panel) and open in the morning (right panel). (Image: CJ Jewell)

Jaltomata
Red-nectar is a novel trait derived within Jaltomata, thought to function as a bird attractant. J. calliantha campanulate (cup-shaped) flower, with red coloured nectar. (Image: J. Kostyun)

Jaltomata
Campanulate flower morphology, where petals are fused and curved to make a cup- or bell-shaped flower, is a derived trait in Jaltomata.
J. dendroidea campanulate flower, with red coloured nectar. (Image: J. Kostyun)

Jaltomata
Rotate, white, bee pollinated flowers are thought to be ancestral in Jaltomata.
J. repandidentata female (pistillate) and hermaphrodite stage flowers. (Image: J. Kostyun)

Jaltomata
J. umbellata short-tubular flowers, with red colored nectar. (Image: J. Kostyun))

Drosophila
Abdominal pigment variation in the Drosophila cardini group (Images: D. Castillo)

Drosophila
A green eye marker (two right flies) can be used to distinguish progeny sired by different fathers, in multiply mated females (Image: D Castillo)
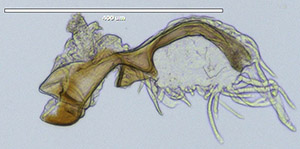
Drosophila
Intromittent organ from Drosophila polymorpha, a member of the cardini group (Image: D. Castillo)
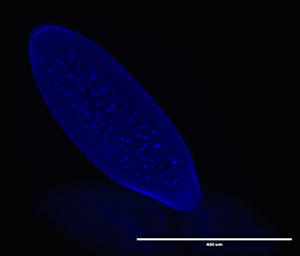
Drosophila
Early mitosis in a Drosophila lumeii × D. virilis F1 hybrid (Image: D. Castillo)